Acidity
High stomach acid levels may occur due to several conditions. Symptoms that high stomach acid levels can cause include bloating, abdominal pain, and unintentional weight loss. Some conditions or infections may cause a person’s stomach to produce high levels of stomach acid, which can contribute to the development of other health conditions.
Gall Stones
Gallstones are hard, pebble-like pieces of material, usually made of cholesterol or bilirubin, that form in your gallbladder. Gallstones can range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball. The gallbladder can make one large gallstone, hundreds of tiny stones, or both small and large stones.
Intestinal Worms
Intestinal worms, also known as soil-transmitted helminthiases, are worm-like parasites that live in the digestive system. They can be caused by infection with nematodes such as roundworms, whipworms, and hookworms. One way to become infected with intestinal worms is by eating undercooked meat from an infected animal, such as a cow, pig, or fish and consumption of contaminated water, soil.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder that primarily affects the large intestine (colon). It is a common condition, characterized by a combination of symptoms that can vary in severity and duration. The exact cause of IBS is not known, but it is believed to involve a combination of factors, including abnormal muscle contractions in the intestine, changes in the gut's sensitivity to certain stimuli, and disturbances in the gut-brain communication.
Jaundice
Jaundice is a condition produced when excess amounts of bilirubin circulating in the blood stream dissolve in the subcutaneous fat (the layer of fat just beneath the skin), causing a yellowish appearance of the skin and the whites of the eyes. This may happen when: There are too many red blood cells dying or breaking down (hemolysis) and going to the liver. The liver is overloaded or damaged.
Peptic Ulcers
Ulcers are caused when there is an imbalance between the digestive juices produced by the stomach and the various factors that protect the lining of the stomach. Symptoms of ulcers may include bleeding. On rare occasions, an ulcer may completely erode the stomach wall. The most common symptom is a burning pain in the stomach, especially between meals or at night.
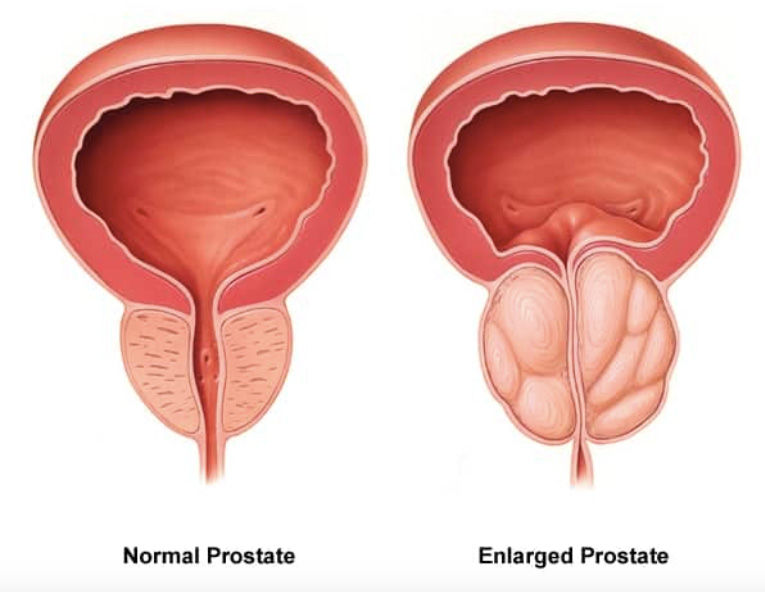
Prostate Enlargement
Prostate Enlargement a condition that can affect how you pee (urinate). The actual cause of prostate enlargement is unknown. Factors linked to aging and changes in the cells of the testicles may have a role in the growth of the gland, as well as testosterone levels. Men who have had their testicles removed at a young age (for example, as a result of testicular cancer) do not develop BPH.







.jpeg)